
Currently, there are a number of reports addressing trends and summaries on security. However, at ElevenPaths we want to make a difference. Our Innovation and Labs team has just launched another release of our own cybersecurity report, summarizing the most significant information from the first half of 2020. The report’s philosophy is providing a global, targeted and useful vision on the most significant data and facts on cybersecurity. It is addressed to cybersecurity professionals and enthusiasts, in a simple and visually-appealing format.
Given all the above, this report aims to summarize latest information on cybersecurity (ranging from security on mobile phones to cyber risk, from the most important news to the most technical ones and the most common vulnerabilities), while covering most aspects of the field, in order to help the readers to understand the risks of the current outlook.
The information here presented is mostly based on the collection and synthesis of internal data that have been contrasted with public information from sources considered to be of quality. Let’s examine below some points that we consider important.
#CyberSecurityReport20H1: General Data
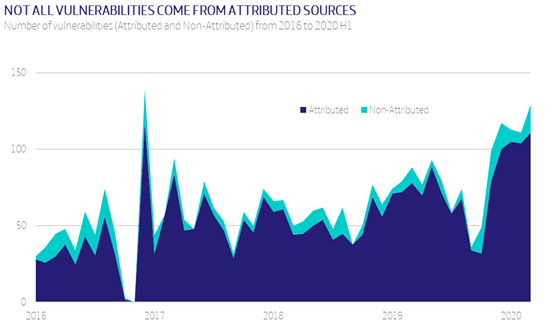
With regard to Microsoft, the total number of bugs discovered and fixed is more than 600 during this half-year. We consider that most of these flaws may come from vulnerabilities found in 0-days or under other circumstances where the author is not known and the vulnerability has not been reported anonymously. In such cases, Microsoft do not attribute the finding to anyone in particular. This difference between attributed and ‘non-attributed’ vulnerabilities (which is not the same as ‘anonymous’) is represented in the following chart.
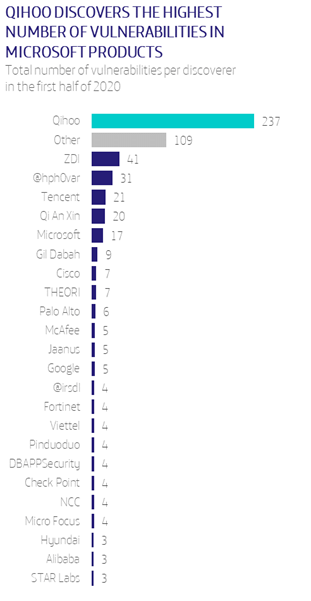
Qihoo is again the most popular with a total of 237 vulnerabilities reported to Microsoft so far this year. But compared to the previous quarter, the numbers have changed substantially.
Qihoo and ZDI report the highest number of vulnerabilities but Google falls heavily. While last half year it was in fifth place, this half year it has fallen to 14th place. Microsoft, which was in third place, falls to sixth. Google goes from discovering 35 in the last half of 2019 to only 5 in this first half of 2020. Microsoft drops from 48 to 17.
Has the pandemic impacted the major vendors? Have they spent less time on vulnerability research? On the contrary, Qihoo not only continues to be the first company to find Microsoft security flaws, but has also substantially multiplied its number, from 79 to 237 this half year.
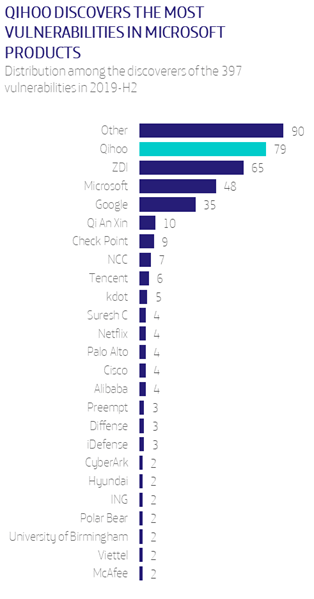
Especially if we compare it to the previous semester:
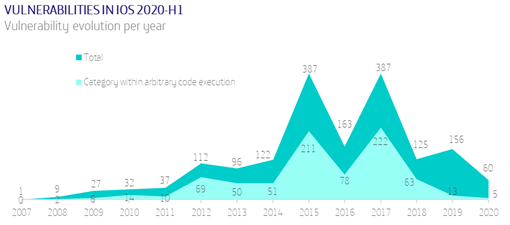
Smartphone Vulnerabilities
This time it is worth noting the statements of the exploit acquisition company, Zerodium, who reported that they were temporarily suspending the purchase of iOS exploits due to a high number of submissions. 13 has not been a good version for iOS.
Alternatively, researchers can submit their findings to Apple’s security reward program (Apple Security Bounty), open to the public since late December last year. Rewards range from $5,000 to $1 million.
In total, 60 CVEs have been patched on iPhone in the previous half year. Of these, 5 were critical and allowed arbitrary code execution. Figures show a clear decrease (although we must wait for the second half of the year), but it has not been a good year for iOS in terms of security.
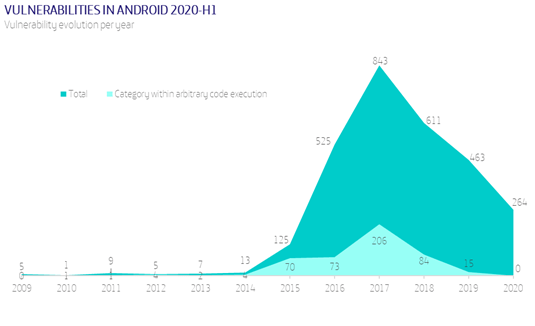
On the other hand, the number of vulnerabilities leaves no room for doubt. Android is a popular platform for vulnerability hunters. This does not mean that it should be considered insecure. It is simply more attractive or interesting for various reasons, including the reward program and the marketing of exploits.
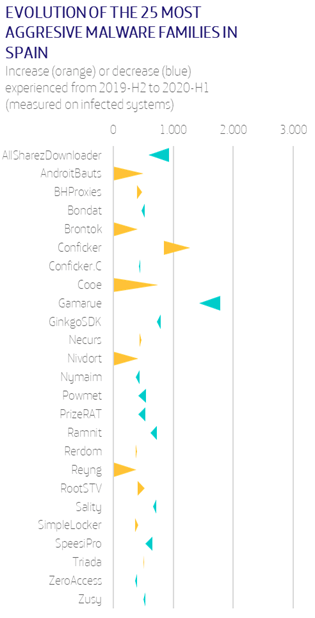
Concerning the BitSight data, in Spain there is a very different leading malware from the other European countries. Malware firms such as AllSharezDownloader and AndroidBauts are leading, while in Europe they are not representative.
More Conclusions
- In the field of smartphone security, the high number of exploits for IOS 13, the announcement of IOS 14 and Android fragmentation have marked the first half of 2020.
- With regard to vulnerabilities and weaknesses, there has been a clear decrease in the figures for vulnerabilities (especially Level-10 ones) but the three vendors with the highest number of associated CVEs remain the same. Regarding weaknesses, those where insufficient or no security configuration is key in the management of user permissions stand out, allowing an escalation of permissions.
- The APT groups have also introduced “SARS-CoV-2” factor in their operations. Some to make a profit, and others in cyberespionage operations to find out “the truth” about the virus.
- This half year Microsoft has exceeded 100 fixed vulnerabilities every month, Qihoo has identified 237, many more than the previous quarter and substantially replacing Microsoft itself and Google, which were the other companies that found the highest number of bugs in Microsoft software.
- BitSight’s data shows that the unbreakable Conficker is once again on the throne of the most aggressive threats, while we also note a worrying fact: In most sectors there is a substantial increase in the time required to neutralize a threat.
The full report can be found here:
The post #CyberSecurityReport20H1: Microsoft Fixes Many More Vulnerabilities, but Detects Far Fewer appeared first on Think Big.